Try our favorite, clean protein powder: See our top pick →
Try our favorite, clean protein powder: See our top pick →
This post contains links through which we may earn a small commission should you make a purchase from a brand. This in no way affects our ability to objectively critique the products and brands we review.
Evidence Based Research To fulfill our commitment to bringing our audience accurate and insightful content, our expert writers and medical reviewers rely on carefully curated research.
Read Our Editorial Policy
Magnesium is an essential mineral required for over 300 processes in the body—but up to two-thirds of the American population is estimated to have inadequate magnesium intake
While magnesium as a whole is needed for healthy brain, nervous system, heart, and muscular function, a specific form called magnesium citrate is most associated with digestive health—especially with relieving constipation.
However, magnesium citrate is good for more than just helping with regularity—learn more about the top benefits of magnesium citrate, typical dosages, and how to supplement with it.
Magnesium citrate is a salt formed by combining magnesium oxide with citric acid, a reaction that creates magnesium citrate and water.
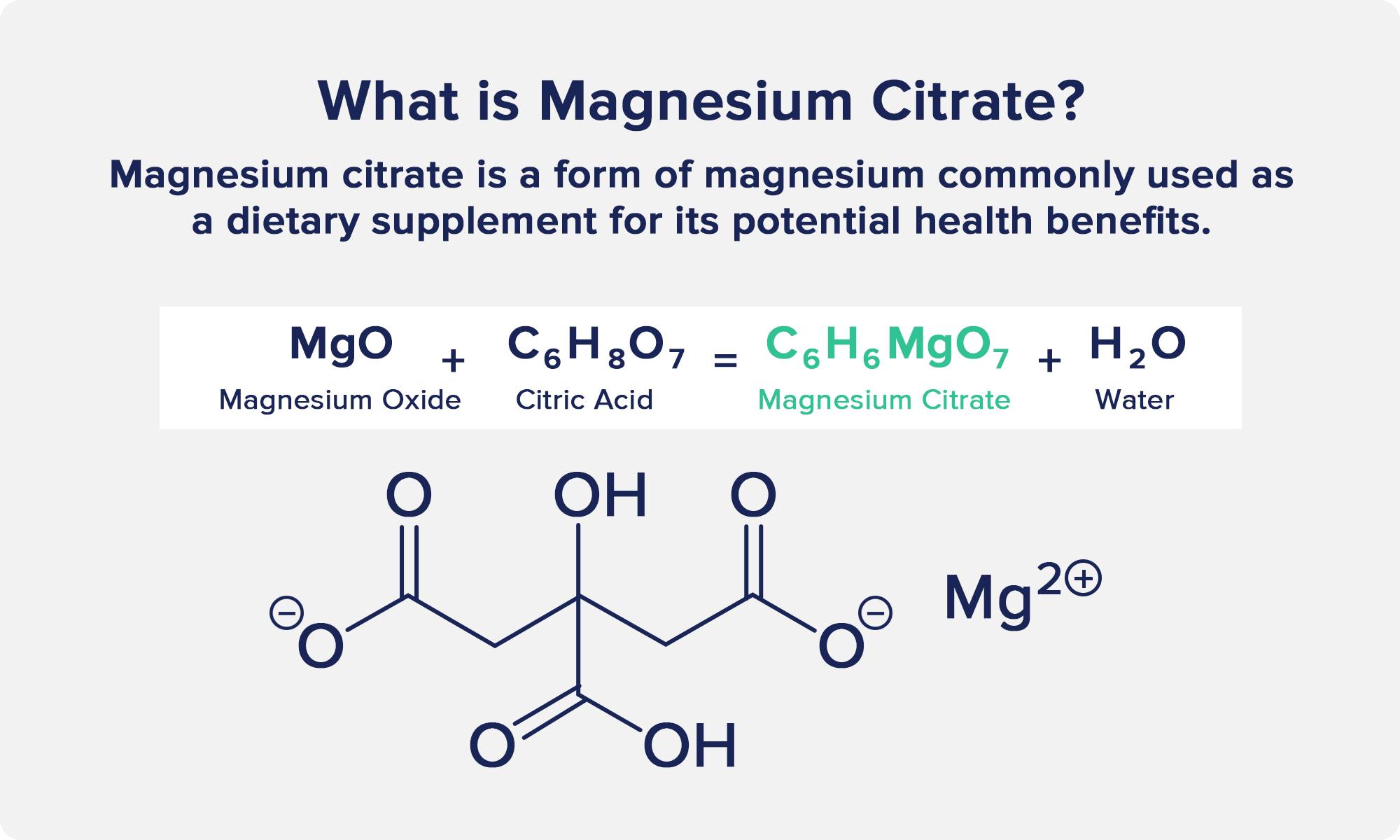
The fact that this reaction forms water is the primary reason why magnesium citrate helps with constipation—it draws water and fluids into the intestines, softening stool for a laxative effect.
Magnesium citrate also dissolves readily in water, so this form is often used in powdered and liquid supplements.
Plus, its ability to dissolve in water helps it to readily absorb into the bloodstream and be used by the body.

Magnesium citrate is known for its digestive-supporting qualities, which is why it’s commonly found as the active ingredient in many over-the-counter laxatives.
To take it back to Chem 101, magnesium is an electrolyte that becomes a positively charged ion (cation) in the body.
When mixed with citrate—a negative ion—these opposite charges create an osmotic effect in the digestive tract.
This means that water enters the intestines and gets absorbed by stool, softening it and helping improve or treat constipation.
For these chemistry-related reasons, other forms of magnesium are typically less effective for increasing regularity.

Magnesium is also essential for muscles and nerves to function properly.
Like calcium and potassium, magnesium ions provide electrical charges that contract muscles and help nerves to send electrical signals throughout the body.
Magnesium can also fight muscle spasms and help with post-exercise recovery because it facilitates the relaxation of contracted muscles.
However, while magnesium citrate can support muscle and nerve function, other forms—like magnesium glycinate—are most commonly used for muscular health.

Magnesium citrate may help to maintain normal heartbeat rhythms, blood pressure, and arterial function.
Without adequate magnesium intake, conditions like arrhythmias, hypertension, and atherosclerosis due to narrowed arterial walls can occur.

Magnesium citrate contributes to bone health by regulating calcium transport across cell membranes and acting as an essential cofactor for vitamin D synthesis—as we know, calcium and vitamin D are both critical for bone growth.
Plus, our bones hold up to 60% of the body’s entire magnesium stores, acting as a magnesium reservoir for the body.
Inadequate magnesium levels also affect bone health by decreasing the activity of bone-building cells called osteoblasts, and research shows that people with osteoporosis are more likely to be magnesium deficient.
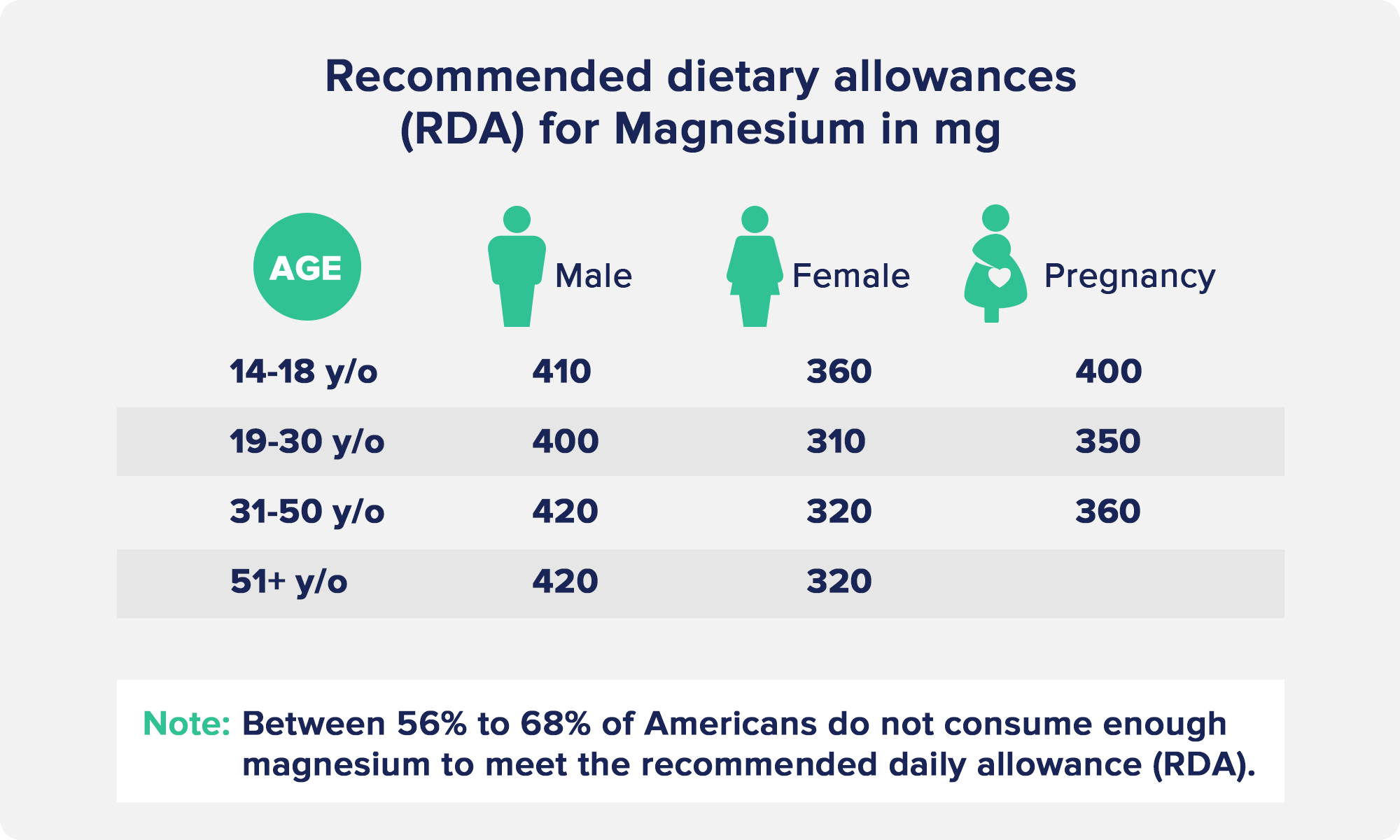
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for magnesium is 400-420mg per day for adult men and 310-320 mg per day for adult women.
If pregnant or breastfeeding, the RDA increases to 350-360mg per day.
If you’re taking magnesium citrate for general health, a dose of 200-400mg per day (in single or divided doses) is typically used.
When starting out with a magnesium citrate powder—a common over-the-counter form used to treat occasional constipation—start with a lower dose of 200mg or less, increasing as needed, and always take magnesium citrate with at least 8oz of water.
People with severe constipation may need higher doses, which are typically recommended by a doctor.
However, taking too much magnesium citrate at once is known to cause digestive problems, including diarrhea and nausea.

Magnesium citrate can be taken in capsule, powder, liquid, or gummy form.
A popular magnesium citrate powder is Natural Vitality Calm, which comes in a raspberry lemonade flavor and contains 325mg of magnesium citrate per serving.
However, you can easily take less if that dose is too high for your tolerance.
Natural Vitality also carries magnesium citrate gummies, providing a smaller dose of 83mg of magnesium citrate per gummy.
In capsule form, two reputable brands include NOW Magnesium Citrate—containing 400mg per three capsules—and Nature’s Way Magnesium Citrate, with a higher dose of 500mg per two capsules.
Yes, you can take moderate doses of magnesium citrate every day.
If you experience digestive side effects, lower the dose until you find an amount that you tolerate better.
For constipation relief, magnesium citrate can cause a bowel movement within 30 minutes to 6 hours after taking it.
It’s best to take magnesium citrate earlier in the day so you don’t have to get up in the middle of the night to use the bathroom.
Although you can take it on an empty stomach, many people experience fewer negative digestive symptoms if taking it with a small meal.
While it doesn’t cleanse the entire body, magnesium citrate can help to cleanse the bowels if you are constipated.
Yes, magnesium citrate is the form of magnesium that works best for constipation relief.
Subscribe now and never miss anything about the topics important to you and your health.