Try our favorite, clean protein powder: See our top pick →
Try our favorite, clean protein powder: See our top pick →
This post contains links through which we may earn a small commission should you make a purchase from a brand. This in no way affects our ability to objectively critique the products and brands we review.
Evidence Based Research To fulfill our commitment to bringing our audience accurate and insightful content, our expert writers and medical reviewers rely on carefully curated research.
Read Our Editorial Policy
Berberine is gaining popularity as a plant-based supplement to manage blood sugar and metabolic function—so much so that some people have dubbed it “nature’s Ozempic,” which is a diabetes drug that is now also being overly prescribed for weight loss.
As berberine is a more natural way to support blood glucose, many are now searching for the best berberine supplements—and we’ve got you covered.
In this article, check out our list of the six best berberine supplements, including our top pick, Enzymedica Berberine, plus options for liquid extracts, people on a budget, and the best berberine for weight loss and blood sugar management.
Best Overall | Highest Dose | Best Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product | Enzymedica | HUM | Solaray |
| Amount of Berberine | 510mg | 1200mg | 535mg |
Cost | $49.49 for 120 servings($0.41/serving) Shop Now | $35 for 30 servings ($1.17/serving) Shop Now | $19.99 for 60 servings ($0.33/serving) Shop Now |
Best for: People looking for a high-quality, sustainably sourced berberine that’s affordably priced.
Enzymedica is best known for its digestive enzymes and gut support supplements, but it’s also our top pick for the best berberine supplement.
Enzymedica Berberine is sustainably sourced from the barberry plant—as opposed to the overharvested goldenseal plant—which grows abundantly and is an eco-friendly way to source berberine.
This supplement also uses a targeted delivery system, and the serving size is only one capsule, which is always appreciated.
With a dose of 510mg of berberine per capsule, this supplement is designed to support healthy blood sugar levels, cardiovascular health, and immune function.
Best for: People who want a higher dose of berberine per serving and just want to take it once per day.
At 1200mg per serving, HUM Nutrition Best of Berberine offers the highest dose of berberine per two-capsule serving on this list.
According to HUM, 1200 milligrams is the most clinically effective dose for lowering blood sugar, supporting gut health, and maintaining a healthy body weight.
This berberine supplement might not be for everyone, as these higher doses are more likely to cause digestive-related side effects when taken all at once.
However, it may be a good choice for people who don’t want to take three split-up doses throughout the day, as this supplement recommends only taking it once per day with food.
We also love that HUM triple-tests their products with third-party labs for purity and quality and is certified by the Clean Label Project.
Best for: People on a budget looking for a high-quality berberine supplement.
At just $0.33 per serving, Solaray Berberine Root Extract Advanced Formula is our top pick for people wanting a berberine supplement on a budget.
With the berberine coming from Indian barberry and Oregon grape (which is actually a shrub and not, in fact, grapes), this berberine supplement is sustainably sourced.
It also contains comparable amounts of berberine to other supplements (535mg per serving) and is third-party tested, vegan, and Non-GMO Project Verified.
For an affordable berberine supplement that doesn’t skimp on quality, Solaray is your best bet.
Best for: People wanting a high-quality berberine supplement with an affordable bulk buying option.
PartiQlar Pure Berberine HCL is a great choice for those looking for an affordable berberine with a moderate dose.
This supplement provides 600mg per one-capsule serving—a middle-of-the-road dose not likely to cause digestive issues—and HCl (hydrochloric acid) is added to aid absorption.
Although it’s already affordable with a one-time purchase ($0.43 per serving), PartiQlar also offers a steep discount when you buy six bottles (bumping it down to just $0.26 per serving and a one-year supply).
We also love that they are third-party tested for purity and have their quality reports readily available on the site.
Best for: People looking for a comprehensive formula (more than just berberine) to support blood sugar management and weight loss.
While all berberine supplements are technically beneficial for lowering blood sugar, 1st Phorm GDA has additional supportive ingredients for doing so—and the name says it all, as GDA stands for “Glucose Disposal Agent.”
These extra nutrients and compounds include chromium, banaba leaf extract, vanadyl sulfate, and cinnamon, all of which have been studied for their role in reducing blood sugar or insulin resistance.
Plus, 1st Phorm GDA contains alpha-lipoic acid and Gymnema sylvestre extract, which may help to support weight loss.
Specifically, Gymnema sylvestre is thought to slow down the absorption of carbohydrates from the intestines into the bloodstream, leading to reduced dietary intake as well as lower blood sugar.
Although this supplement is about double the price per serving of others, you get the benefit of six additional compounds to support weight loss and blood sugar management, which may make it well worth it for some.
Best for: People who experience digestive problems from berberine; those looking for a more absorbable form of berberine.
NOW Berberine Glucose Support is a great option for supporting the absorption and utilization of berberine, as the compound is known to have limited bioavailability on its own.
In addition to 400mg of berberine per capsule, this NOW supplement also contains capric acid and medium-chain triglycerides, which are thought to boost berberine’s bioavailability and lessen any potential digestive symptoms from the compound.
However, this supplement is not vegan or vegetarian, as it contains bovine gelatin and beeswax, as well as caramel coloring in the capsule, which some people try to avoid.
Overall, this NOW Berberine supplement is a good choice if you experience gastrointestinal upset from taking berberine or want to ensure that you are absorbing the compound well.
Berberine works primarily by activating an enzyme called AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which acts like a metabolic master switch that reduces blood sugar and regulates metabolism.
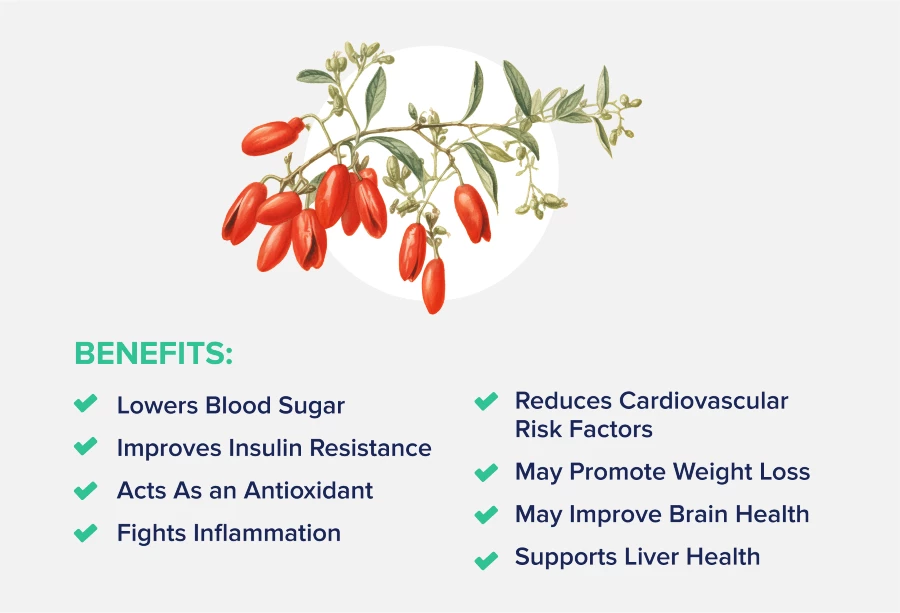
Berberine is most well-known for its ability to reduce blood sugar and insulin resistance, which may reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
It may also reduce high cholesterol and lipid levels and support liver function, brain health, and weight loss.
Berberine is an alkaloid compound that exerts antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity, which translates to several health benefits, including:
Although berberine has plenty of benefits, there are also some potential downsides to be aware of.
Berberine is generally safe in moderate doses—such as 250-500mg, three times per day—but higher or excessive doses may cause side effects.
The most common side effects of berberine are gastrointestinal-related, including gas, bloating, indigestion, diarrhea, or constipation—however, these are often fixed by taking smaller doses or splitting it up between three meals.
As one of the leading benefits of berberine is lowering blood sugar, it can also cause hypoglycemia (too-low blood sugar) in some people.
Berberine has the potential to interact with several medications (especially those for lowering blood sugar), so check with your healthcare provider if you’re unsure.
Lastly, it’s not recommended to take berberine if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Although berberine comes from different plants (goldenseal, barberry, Oregon grape, etc.), they aren’t thought to be more or less effective depending on which plant they come from.
However, some supplements may contain additional ingredients to support the absorption and utilization of berberine—like NOW Berberine Glucose Support, which adds medium-chain triglycerides to boost bioavailability.
Most berberine supplements come in doses of 400-500mg per serving and can be taken up to three times per day with meals.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take berberine, and people with diabetes or those taking medications for diabetes will need to speak with their healthcare provider first, as berberine can also lower blood sugar.
The most common side effects of berberine are gastrointestinal, including nausea, gas, diarrhea, or constipation—especially if taken in doses that are too high (more than 500mg at a time).
Berberine and berberine HCl are very similar—the only difference is that berberine is a naturally occurring compound derived from plants like barberry, while berberine HCl is a chemically made supplement that combines berberine with hydrogen chloride, which may make it more stable.
Subscribe now and never miss anything about the topics important to you and your health.