Try our favorite, clean protein powder: See our top pick →
Try our favorite, clean protein powder: See our top pick →
Evidence Based Research To fulfill our commitment to bringing our audience accurate and insightful content, our expert writers and medical reviewers rely on carefully curated research.
Read Our Editorial Policy
With its use dating back millennia, berberine is a powerful plant compound that has been utilized for both ancient and modern healing practices.
Found in several plants, including barberry, Chinese goldthread, and goldenseal, berberine is a potent antioxidant that has recently grown in popularity due to its metabolism-boosting and blood-sugar-lowering effects.
In this article, learn more about the leading berberine benefits and how it works in the body, from supporting glucose metabolism to promoting weight loss to improving liver function.
Berberine is an alkaloid compound—a nitrogen-containing, plant-derived molecule that exerts antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory activity.
Alkaloids are produced in plants as a defense response to environmental stressors, providing pharmacological-like support in the human body.

Berberine works primarily by activating an enzyme called AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which acts like a sensor inside cells for low energy (ATP) levels.
When AMPK senses low energy, it works quickly to restore it inside cells, which it does by redirecting metabolism to take sugar in the form of glucose from the blood and pull it into cells to be used for energy.
Essentially, AMPK acts as a “metabolic master switch” in the body—and berberine activates this switch regardless of what energy levels are, which helps to regulate both blood sugar levels and body weight.
With these antioxidant and AMPK-activating actions, berberine is thought to provide several health benefits, from lowering blood sugar and cholesterol to promoting weight loss and brain function—let’s take a closer look.
One of the top ways that berberine benefits health is through its ability to manage high blood glucose and insulin resistance—two of the leading risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
As mentioned, berberine activates the AMPK pathway to pull glucose from the blood, directly lowering blood sugar.
In addition, berberine has been found to increase glucokinase activity, an enzyme that controls insulin release and is often referred to as our “glucose receptor.”
In a 2021 meta-analysis, researchers compiled data from 46 trials looking at the effects of berberine on people with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes.
They found that supplementing with berberine significantly reduced hemoglobin A1C (a common biomarker of diabetes), fasting glucose, and post-meal glucose levels compared to control groups.
Berberine treatment also improved insulin resistance—a state when the body stops responding to insulin, the hormone that shuttles glucose from the blood into cells.
Notably, both human and animal studies have found that taking 500mg of berberine three times per day is comparably effective to leading pharmaceutical diabetic medications (which is why it’s been dubbed “nature’s Ozempic”) that also target the AMPK pathway.
Berberine benefits health by acting as an antioxidant, which helps to fight oxidative stress—an accumulation of harmful compounds (like free radicals and reactive oxygen species) that damage cells, proteins, and DNA.
Oxidative stress is a leading contributor to accelerated aging and chronic disease—and compounds like berberine may be able to help neutralize the harm.
Research has shown that berberine reduces markers of oxidative stress (like the compound malondialdehyde, or MDA) and increases levels of other antioxidants in the body—including our body’s master antioxidant, glutathione.

While it can occur for several reasons, hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) is known to worsen or exacerbate oxidative stress—therefore, berberine’s free-radical-fighting and blood-sugar-lowering abilities act as a one-two punch here.
At the root of many diseases is chronic inflammation—and berberine may be able to help lower it.
Research has found that berberine reduces several pro-inflammatory compounds or markers of inflammation, including C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α).
Because of these inflammation-fighting effects, berberine is thought to play a role in reducing the risk of several chronic diseases or their symptoms, including cardiovascular disease, cognitive disorders, and liver disease.
Berberine is thought to improve several risk factors related to heart disease, including high cholesterol, blood pressure, triglycerides, and inflammation.
In the previously mentioned meta-analysis of 46 trials, berberine was also found to significantly reduce total cholesterol, triglycerides, and LDL (“bad cholesterol”) while increasing HDL (“good cholesterol”).
Berberine may also benefit heart health by increasing the production of nitric oxide—a vasodilating compound that relaxes blood vessels and supports healthy blood pressure.
In a 2015 meta-analysis, researchers found that combining berberine with lifestyle interventions lowered blood pressure in people with hypertension more than placebo pills or lifestyle intervention alone.
However, other reviews on berberine and hypertension have concluded that there isn’t enough evidence yet to recommend berberine as a blood-pressure-lowering agent.
Although weight gain is complex and multifactorial, inflammation, high blood sugar, and insulin resistance are all intricately linked with obesity—and, as we’ve seen, berberine may help to support these processes.
Research has also uncovered that berberine reduces adipocyte (fat cell) growth by regulating the activity of specific genes involved in that process.
In a study with mildly overweight adults, people who supplemented with berberine for one month lost weight and had increased brown adipose tissue activity—also known as brown fat, this healthy type of fat tissue is more metabolically active and increases energy expenditure.
However, not all studies have reported weight loss benefits from taking berberine—in this 2020 meta-analysis of 12 trials, researchers found that berberine supplementation reduced average waist-to-hip ratios but had no effect on BMI or body weight.
Berberine can cross the highly selective blood-brain barrier and facilitate the clearing of dysfunctional neurons by inducing autophagy—our body’s way of removing or recycling damaged cells and cell parts.
While we don’t have research looking at the effects of berberine in humans with Alzheimer’s disease, a review of 15 animal studies found that berberine significantly improved memory in animals with cognitive impairment.
The mechanisms behind these benefits were multi-fold, including lowering neuroinflammation, fighting oxidative stress, and reducing amyloid protein buildup (a common biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease or dementia).
While we don’t know for sure if these results would translate to humans, the animal-based research is promising for using berberine to support brain health or cognitive function.
Last but not least, berberine has been shown to improve liver function, including reducing fatty liver (hepatic steatosis).
In addition to lowering liver fat levels, which is a precursor to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), berberine has also been found to reduce liver fibrosis—a buildup of scar tissue in the liver that leads to cirrhosis.
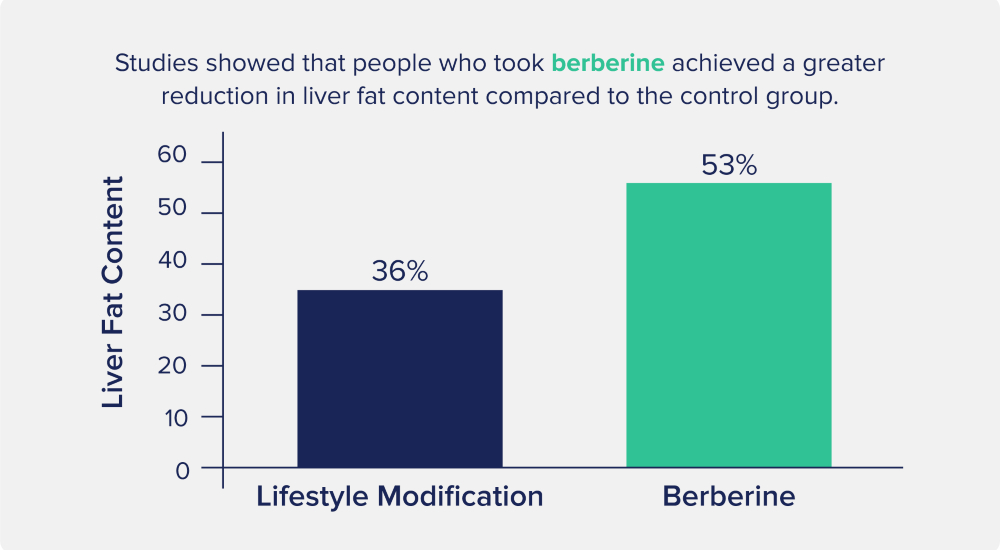
Research has shown that people with NAFLD who took 1500mg of berberine per day for 16 weeks had significantly improved liver health, especially when paired with lifestyle changes.
Specifically, the group with berberine supplements added had a decrease in liver fat content by 53%, compared to a 36% reduction in the lifestyle modification group.
Although berberine has plenty of benefits, there are also some potential downsides to be aware of.
Berberine is generally safe in moderate doses—such as 250-500mg, three times per day—but higher or excessive doses may cause side effects.
The most common side effects of berberine are gastrointestinal-related, including gas, bloating, indigestion, diarrhea, or constipation—however, these are often fixed by taking smaller doses or splitting it up between three meals.
As one of the leading benefits of berberine is lowering blood sugar, it can also cause hypoglycemia (too-low blood sugar) in some people.
Berberine has the potential to interact with several medications (especially those for lowering blood sugar), so check with your healthcare provider if you’re unsure.
Lastly, it’s not recommended to take berberine if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Berberine is an alkaloid compound that provides antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity, which is beneficial for heart, liver, brain, and metabolic health.
Berberine works primarily by activating an enzyme called AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which acts like a metabolic master switch that reduces blood sugar.
When berberine activates the AMPK pathway, it takes glucose from the blood into cells, directly lowering blood sugar.
In addition, berberine has been found to increase glucokinase activity, an enzyme that controls insulin release and is often referred to as our “glucose receptor.”
Berberine is generally safe in moderate doses, but higher or excessive doses may cause some side effects.
First, berberine has a high potential to interact with other medications—especially those designed to lower blood sugar—so check with your healthcare provider if you’re unsure.
Another potential berberine side effect is gastrointestinal upset, which typically occurs if you take it at high doses.
Splitting it up to three doses per day with meals is a way to combat these effects.
Although the dosage will vary by individual, the available research uses anywhere from 900 to 2,000mg of berberine daily, split into three or four doses with meals.
For most people, it is safe to take berberine daily. However, if you take medications for blood sugar, you should talk to your doctor to find a dosage that is right for you.
Berberine may help with weight loss by fighting inflammation, reducing insulin resistance, reducing adipocyte (fat cell) growth, and increasing brown fat activity—a healthy type of fat tissue that burns more calories.
However, while some studies have shown benefits of berberine and weight loss, the research on berberine and fat reduction is not conclusive and more studies are needed.
Although you may see immediate results with lowering blood sugar, berberine is not an overnight magic pill when it comes to weight loss.
It may take 1-3 months or longer to see any noticeable weight loss effects from berberine.
Conversely, you may experience blood sugar-lowering benefits from berberine immediately.
Subscribe now and never miss anything about the topics important to you and your health.