Try our favorite, clean protein powder: See our top pick →
Try our favorite, clean protein powder: See our top pick →
Evidence Based Research To fulfill our commitment to bringing our audience accurate and insightful content, our expert writers and medical reviewers rely on carefully curated research.
Read Our Editorial Policy
At one point or another, we’ve all experienced the unpleasant feelings of anxiety—that gut-wrenching, cold-sweaty, panic-inducing, downward-spiral feeling.
Whether it’s a quick bout of nerves before that big presentation or the more chronic kind that stays with you day after day, many people rightfully wonder if there are natural ways to treat anxious thoughts and feelings without taking prescription medications.
L-theanine is one such natural compound, functioning similar to anti-anxiety drugs without the serious side effects and addictive qualities.
By promoting calm energy, better concentration, and improved mental focus, L-theanine acts as an anxiolytic—a medication or supplement that reduces anxiety—that you can get from both supplements or sipping on green tea.
If you’re part of the one-third of American adults who have dealt with anxiety at some point in their lives, keep reading to find out how L-theanine affects anxiety and the brain, how much L-theanine to take to improve anxiety, and when to take it for the best results.
L-theanine is an amino acid found primarily in green and black tea, with white tea and some mushrooms also containing the compound in smaller amounts.
In contrast to most amino acids, L-theanine is unique because it doesn’t function as a building block to proteins in the body.
Rather, it’s characterized as a non-dietary, non-essential amino acid because not many foods contain L-theanine, and our bodies don’t require it to survive.
Although people have been utilizing green tea for over 4,000 years to promote relaxed mental focus—ever wondered why Buddhist monks are so calm—scientists didn’t isolate the compound L-theanine until 1949.
In recent years, researchers have looked to L-theanine for its potential role as a nootropic.
Also known as smart drugs or cognitive enhancers, nootropics are compounds that boost brain function and increase alertness.
As most nootropics do, L-theanine promotes better mental energy, memory, and a relaxed flow state.
However, if you suffer from anxiety, you may wonder if L-theanine’s energy-boosting nootropic qualities will worsen your anxiety instead of improving it.
Fortunately, that is not the case—L-theanine uniquely promotes calm mental energy without jitters, making it a perfect compound for people with anxiety.
As a natural anxiolytic, L-theanine has been studied for its role in reducing symptoms of anxiety and stress.
In a randomized controlled trial published in the journal Nutrients, adults who took 200mg of L-theanine for four weeks exhibited significantly improved scores on subjective measures of anxiety and stress.
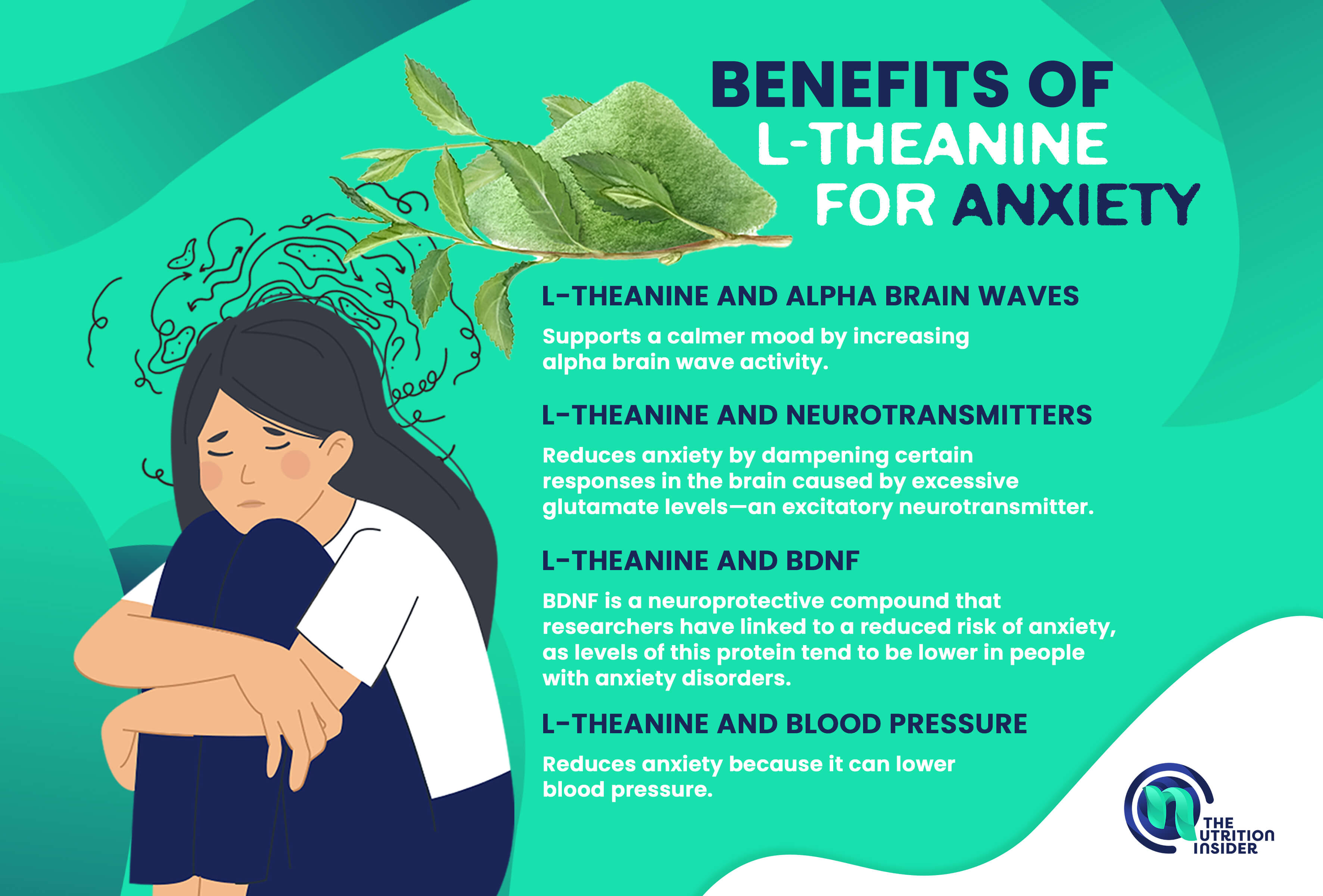
Many mechanisms are at the root of these benefits, including L-theanine’s ability to promote calm brain waves, regulate neurotransmitters and neuron growth, and lower blood pressure.
First, L-theanine supports a calmer mood by increasing alpha brain wave activity—a unique type of brain wave that is present during periods of calm and content focus, like meditation, working on something you genuinely enjoy, or even daydreaming.
Alpha brain waves promote relaxation and alertness simultaneously, and researchers have studied them for their role in reducing anxiety and depression.
L-theanine also reduces anxiety by dampening certain responses in the brain caused by excessive glutamate levels—an excitatory neurotransmitter.
While excitatory responses are helpful when we need a quick jolt of energy, sometimes people with anxiety can take it too far, leading to increased stress hormones and higher blood pressure and heart rate.
L-theanine counteracts these responses by increasing the activity of GABA—an inhibitory neurotransmitter that essentially acts as the antithesis of glutamate.
When GABA levels are higher, glutamate levels will naturally decrease, as these two chemicals maintain a delicate see-saw balance in the brain.
At the same time, L-theanine also directly reduces glutamate by binding to glutamate receptors in the brain.
When L-theanine binds to these receptors instead of allowing glutamate to do so, overall glutamate levels decrease, and more GABA can circulate to promote a calming effect.
Another benefit of L-theanine is its ability to increase brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a necessary protein for maintaining and growing new neurons in the brain—a process called neurogenesis.
BDNF is a neuroprotective compound that researchers have linked to a reduced risk of anxiety, as levels of this protein tend to be lower in people with anxiety disorders.
Lastly, L-theanine reduces anxiety because it can lower blood pressure.
These two conditions have a bidirectional relationship, as anxiety may lead to high blood pressure, and high blood pressure can also trigger feelings of anxiety.
Stress and anxiety are known to increase blood pressure by constricting blood vessels.
L-theanine fights back on this by reducing the central nervous system’s stress response and stimulating nitric oxide production—a compound that dilates blood vessels and lowers blood pressure, which may reduce anxiety.
As the compound is found naturally in green tea, L-theanine is considered a safe supplement.
Although the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not regulate supplements, it has granted L-theanine GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) status, with minimal side effects reported.
Plus, L-theanine has extremely low toxicity, as seen in an animal study where no toxic effects were seen even at doses of 4,000mg per kg of body weight for 13 weeks.
Some people wonder if L-theanine can worsen anxiety based on some reported cases of increased anxiety symptoms after taking it.
However, this is typically the case only when taking excessive doses of L-theanine, whereas doses of 50-200mg likely would not increase anxiety.
Another common reason why L-theanine might increase anxiety in certain people is if they consume it alongside excessive caffeine, especially if you are sensitive to caffeine.
Lastly, L-theanine may interact with certain medications—especially stimulant drugs or those for high blood pressure.
To be on the safe side, check with your doctor before taking L-theanine if you are taking any prescription medications.
L-theanine is thought to boost levels of the neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine—two feel-good brain chemicals that lower the overall stress response, improve mood, and promote relaxation.
However, most research on L-theanine and serotonin has been done with animals.
Studies with humans are often inconsistent regarding whether or not L-theanine increases serotonin—some research even shows that L-theanine may occasionally decrease serotonin brain levels, but this is usually seen with higher doses.
As panic attacks are a form of extreme anxiety, L-theanine may also help with panic symptoms by acting as a mild calming sedative.
However, L-theanine should not be considered a treatment for panic attacks—it would likely be more beneficial when taken preventatively.
Because of L-theanine’s stress-reducing and calming properties, the compound is also thought to benefit sleep.
In a randomized controlled trial, adults who took L-theanine had significantly improved sleep quality, including reductions in sleep disturbances and sleep latency (the time it took to fall asleep).
Unlike over-the-counter or prescription sleeping pills, L-theanine promotes sleepiness and relaxation in a non-sedative way, making it a safe and natural sleep aid option.
Although it can vary from person to person, most research supports using 200mg as a safe and effective L-theanine dosage for anxiety.
However, some may experience the benefits at doses as low as 50mg.
Products like Qualia’s Qualia Mind—a nootropic for mental performance—include L-theanine at doses of 200mg.
Another nootropic supplement, Onnit’s Alpha Brain, uses L-theanine in an unspecified amount as part of their “Onnit Flow Blend.”
But there is currently no official L-theanine dosage guideline in the United States, although doses of up to 400mg per day are typically safe and well-tolerated.
Some people may experience fatigue or drowsiness at doses of 500mg or more.
You can also get L-theanine directly from tea, albeit in smaller amounts—one cup of green tea is estimated to contain between 8-25mg of L-theanine, with differences in L-theanine content based on brewing times.
People typically notice a calming effect within 30 to 40 minutes after taking 100-200mg of L-theanine, with the effects lasting up to 8 hours.
The best time to take L-theanine will depend on what your intended goal for using it is.
If you’re taking L-theanine to help with anxiety, it’s recommended to take two split-up doses in the morning and night—for example, 100mg at breakfast and 100mg at dinner.
To boost mental focus or energy, try taking L-theanine first thing in the morning, ideally about 30 minutes before breakfast.
Conversely, to help support better sleep, a 50-200mg dose of L-theanine 30-60 minutes before bed would be best.
Many people with anxiety avoid coffee like the plague—and with good reason, as caffeine can significantly increase anxious feelings.
However, combining L-theanine and coffee can amplify L-theanine’s nootropic abilities without causing stressful jitters.
This combination promotes increased cognitive performance and higher energy levels while promoting a state of calm contentment that supports memory and neuron growth.
A study published in Nutritional Neuroscience found that young adults who combined L-theanine with caffeine had better alertness, reduced tiredness, and more accurate reaction times during cognitive and attention tasks.
However, the study did not measure anxiety or stress-related behavior.
Dasdelen MF, Er S, Kaplan B, et al. A Novel Theanine Complex, Mg-L-Theanine Improves Sleep Quality via Regulating Brain Electrochemical Activity. Front Nutr. 2022;9:874254. Published 2022 Apr 5. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.874254
Giesbrecht T, Rycroft JA, Rowson MJ, De Bruin EA. The combination of L-theanine and caffeine improves cognitive performance and increases subjective alertness. Nutr Neurosci. 2010;13(6):283-290. doi:10.1179/147683010X12611460764840
Hidese S, Ogawa S, Ota M, et al. Effects of L-Theanine Administration on Stress-Related Symptoms and Cognitive Functions in Healthy Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2019;11(10):2362. Published 2019 Oct 3. doi:10.3390/nu11102362
Janke KL, Cominski TP, Kuzhikandathil EV, Servatius RJ, Pang KC. Investigating the Role of Hippocampal BDNF in Anxiety Vulnerability Using Classical Eyeblink Conditioning. Front Psychiatry. 2015;6:106. Published 2015 Jul 24. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2015.00106
Subscribe now and never miss anything about the topics important to you and your health.
1 Comment
i have sever anxiety and use lthianine all th etime. i typicallly take 100 mg every few hrs during the day. i take 200 at night before bed. i also use vitamin c . that helps also.