Try our favorite, clean protein powder: See our top pick →
Try our favorite, clean protein powder: See our top pick →
Evidence Based Research To fulfill our commitment to bringing our audience accurate and insightful content, our expert writers and medical reviewers rely on carefully curated research.
Read Our Editorial Policy
If you have irritable bowel syndrome or unexplained gastrointestinal symptoms after eating, you may have come across the low FODMAP diet in an attempt to improve your digestive troubles.
While the low FODMAP diet does eliminate potentially gut-disrupting foods, it can often be difficult to follow—especially in the beginning.
Fortunately, we’re here to help—keep reading to learn more about what FODMAPs are, tips for low FODMAP meal prep, and an easy-to-follow low FODMAP diet meal plan.
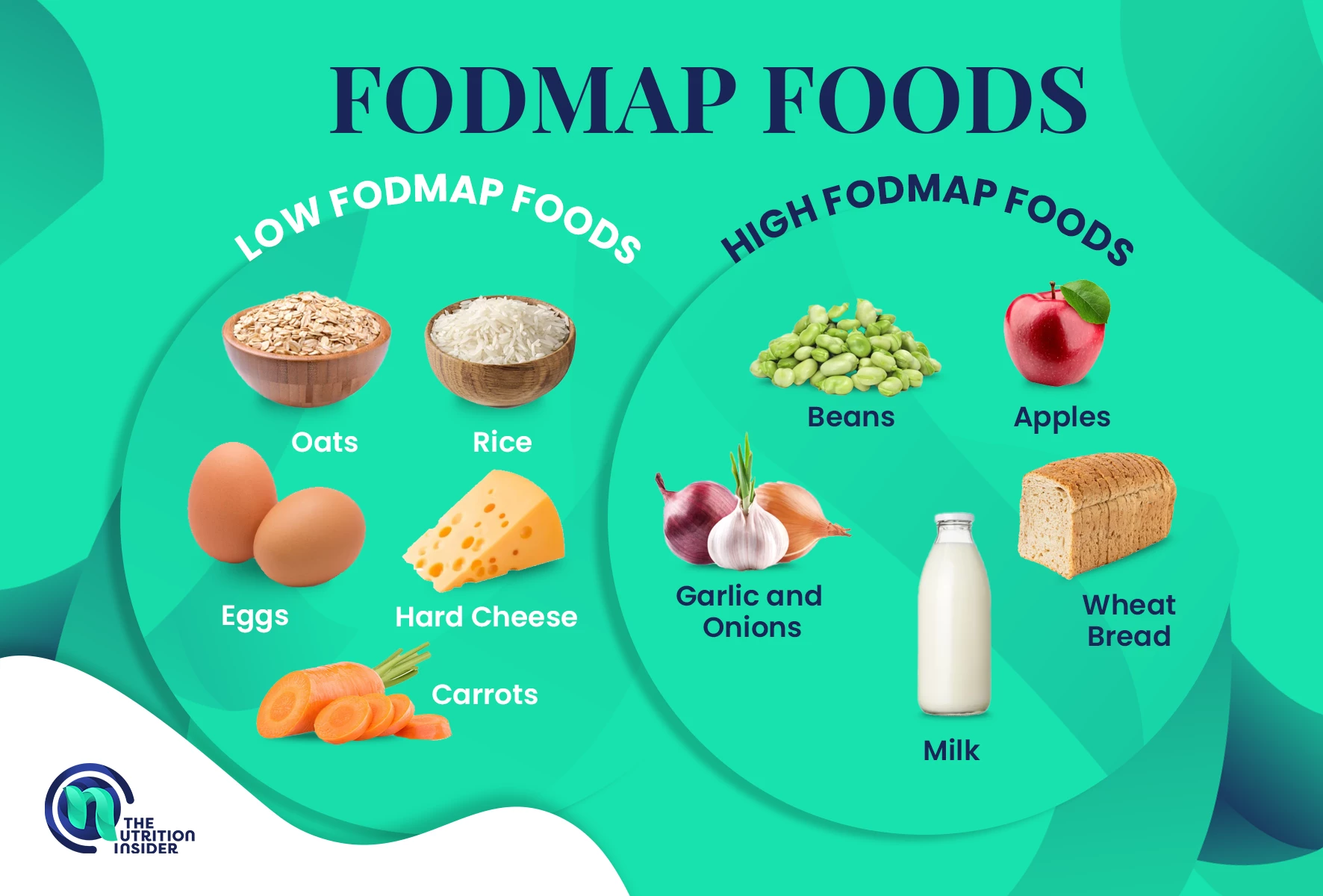
FODMAP is an acronym for Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols.
FODMAPs are all types of carbohydrates that can trigger digestive symptoms in some people, as they are often poorly absorbed by the small intestine.
Specific types of carbohydrates with high FODMAP levels include fructose, fructans, lactose, galactans, and polyols.
FODMAPs are found in many common foods, especially certain fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and legumes.
Some of the most common high FODMAP foods include:
As most, but not all, of these foods are nutritious and contain healthy amounts of fiber, it’s not always recommended to be on a low FODMAP diet plan for life.
Many people find digestive comfort after following this elimination diet for 4-6 weeks, then reintroducing foods one at a time.
Although the list of high FODMAP foods to avoid may seem daunting, there are some helpful tips for making a low FODMAP meal plan:
Although the list of high FODMAP foods to avoid seems long, there are also plenty of low FODMAP grocery staples to add to your list.
Many prepackaged or ready-to-eat foods can be challenging to eat because of the variety of ingredients and potentially high FODMAP ingredients.
Some of our favorite on-the-go, low FODMAP snacks are GoMacro Bars, with 7 of their 15 bars being Certified FODMAP Friendly.
Other low FODMAP foods include:
| Breakfast | Scrambled or poached eggs with potato-and-tomato hash and shredded cheddar cheese | ½ cup of oatmeal with lactose-free milk, unripe banana, peanut butter, and 10 blueberries |
| Lunch | Salad topped with chicken or fish, walnuts, parmesan cheese, and olive oil-based dressing | Sandwich with gluten-free bread, organic deli turkey, tomato, lettuce, mayo, and mustard |
| Dinner | Roasted wild-caught salmon marinated with soy sauce and sesame oil, served with bok choy and brown rice or quinoa | Burrito bowl with ground beef or turkey seasoned with cumin and paprika, rice, tomatoes, jalapeno peppers, lettuce, cilantro, and cheddar cheese |
| Snacks | Hard-boiled egg plus a string cheese GoMacro Bar plus a kiwi or mandarin oranges | Baby carrots and rice cakes with peanut butter Mixed low FODMAP nuts (pine nuts, walnuts, macadamia nuts, small amounts of almonds) |
People with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or those who regularly experience gastrointestinal symptoms (like diarrhea, bloating, abdominal pain, cramping, or gas) after eating certain foods may benefit from a low FODMAP diet.
Research suggests that up to 80% of people with IBS experience symptom relief when following a low FODMAP diet.
There are many low FODMAP foods that you can enjoy on this diet, including many types of animal protein, low-fructose fruits, some vegetables, lactose-free dairy products, hard cheeses, and gluten-free grains.
Despite the word “diet” being in its name, the low FODMAP diet is not designed for you to lose weight—it’s designed to help manage IBS and improve digestive symptoms.
However, some people may experience some weight loss on the low FODMAP diet because of the food restrictions that make it challenging to eat out at restaurants or consume prepackaged foods.
Gluten-free bread that doesn’t contain beans, lentils, or chickpeas is safe to eat on a low FODMAP diet.
The most commonly used flours in gluten-free bread are cornstarch, rice flour, tapioca starch, and potato flour.
Some people on a low FODMAP diet also do fine with sourdough bread—especially homemade—because the sourdough starter helps break down the fructans from the flour.
Yes, coffee is technically low FODMAP, but can still be an irritant to the digestive system for many people.
However, many things that people typically add to coffee, like creamers, milk, and sugar substitutes, are not low FODMAP and should be avoided.
If you don’t like black coffee, adding lactose-free milk or small amounts of oat or almond milk should be fine, as well as small amounts of brown sugar, raw sugar, stevia, or maple syrup.
Small amounts of chocolate are okay to consume when following a low FODMAP diet.
Dark chocolate will be better tolerated than lactose-containing milk chocolate—plus, dark chocolate is more nutritious and contains beneficial antioxidants.
However, you’ll want to check the ingredient list and avoid any chocolate that contains inulin or chicory root, as well as high FODMAP sweeteners like high fructose corn syrup, honey, agave syrup, and sugar alcohols like sorbitol, mannitol, maltitol, isomalt, or erythritol.
Yes, peanut butter is low FODMAP—just ensure there is no high-fructose corn syrup, honey, agave, or sugar alcohols added.
Yes, eggs—as well as most animal proteins—are low FODMAP, making them an excellent choice for adding protein to meals or snacks.
Altobelli E, Del Negro V, Angeletti PM, Latella G. Low-FODMAP Diet Improves Irritable Bowel Syndrome Symptoms: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2017;9(9):940. Published 2017 Aug 26. doi:10.3390/nu9090940
Bellini M, Tonarelli S, Barracca F, et al. A Low-FODMAP Diet for Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Some Answers to the Doubts from a Long-Term Follow-Up. Nutrients. 2020;12(8):2360. Published 2020 Aug 7. doi:10.3390/nu12082360
Subscribe now and never miss anything about the topics important to you and your health.