Talk to a Registered Dietitian and use INSIDER20 for 20% off!
Talk to a real Dietitian for only $99: Schedule Now
This post contains links through which we may earn a small commission should you make a purchase from a brand. This in no way affects our ability to objectively critique the products and brands we review.
Evidence Based Research To fulfill our commitment to bringing our audience accurate and insightful content, our expert writers and medical reviewers rely on carefully curated research.
Read Our Editorial Policy
If you’re like me, you see the word phosphatidylserine and it scrambles your brain like Supercalifragilisticexpialidocious did the first time you heard Dick Van Dyke and Julie Andrews singing about it in Mary Poppins.
But fear not! We are here to unscramble your brain and give you the details on this phospholipid.
Phospholipids are a class of lipids that are a major component of cell membranes. They are fatty substances that protect nerve cells in your brain and help them communicate with each other.
Unfortunately, as you age, the effectiveness of this fatty goodness declines, which can affect your memory and cognitive function. Fortunately, there are ways we can increase it. In this article, we will explore what phosphatidylserine is, its benefits, dietary sources, and potential side effects of phosphatidylserine.
Phosphatidylserine (PS) is a phospholipid that plays a critical role in the function of cells throughout the body, especially in brain cells. It makes up 10-20% of the phospholipid pool forming that nerve cell membrane bilayer.
Research reveals that phosphatidylserine levels steadily decline as part of normal aging. This age-associated deficiency in the brain has been linked to structural and functioning changes.
Restoring phosphatidylserine levels through supplementation may help maintain memory, learning ability, concentration, and other mental functions during healthy aging.
We are going to get a littlescience-y here, but bear with us…
Phosphatidylserine consists of a glycerol backbone, two fatty acid chains, a phosphate group, and a serine molecule. It is an essential component of the phospholipid bilayer in cell membranes and plays a critical role in maintaining the fluidity and integrity of cell membranes.
An article posted in 2022 boldly states, “Phosphatidylserine improves the cognitive function of the brain.” You have our attention.
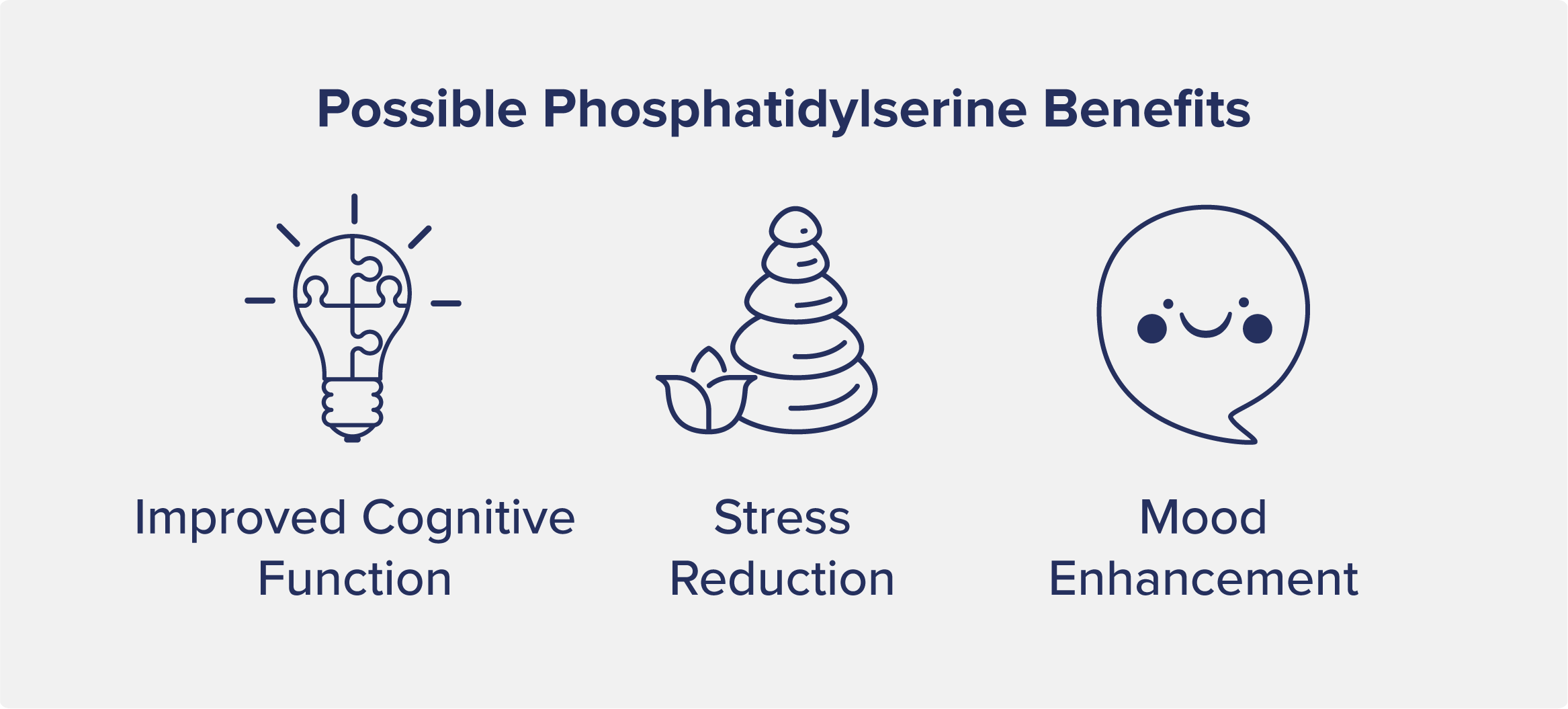
Multiple studies have shown that taking a phosphatidylserine supplement significantly improved cognitive decline caused by aging. This is done because phosphatidylserine is a key component of brain cell membranes.
Although phosphatidylserine can be synthesized in the body, research shows brain phosphatidylserine levels decrease by 15-20% between young adulthood and old age. The drop in phosphatidylserine disturbs membrane fluidity and critical signaling roles.
Enhancing and restoring membrane fluidity may counteract age-related brain function, boosting memory, learning, and improve mental focus. Plus, it helps to improve focus in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
Phosphatidylserine could potentially mitigate the body’s response to chronic stress by lowering cortisol levels, a hormone linked to stress. Elevated cortisol levels are linked with heightened anxiety, high blood pressure, immune suppression, mild cognitive impairment (potentially severe depending on the extent of the problem), and other detrimental effects of chronic stress.
Phosphatidylserine’s ability to regulate cortisol levels might contribute to its calming effect on the body. When combined with other substances like omega-3 fatty acids, phosphatidylserine may offer a holistic approach to managing stress-related mood disturbances.
Taking phosphatidylserine as a dietary supplement has been explored for its mood-enhancing effects, particularly in cases of major depression and anxiety.
Phosphatidylserine supplementation may offer a glimmer of hope for individuals grappling with a mental health condition.
While it’s not a standalone treatment for major depression, when used with conventional treatments, it could lead to a greater improvement in mood and depression.
Phosphatidylserine’s impact on mood regulation is believed to stem from its role in neurotransmitter function and cell membrane stability.
Two of the most crucial neurotransmitters for mood regulation are dopamine and serotonin. By ensuring proper function and signaling of these neurotransmitters, phosphatidylserine can indirectly influence mood.
Before starting any supplementation, make sure you seek advice from a healthcare professional.
We now know that phosphatidylserine is a naturally occurring phospholipid that is integral to cell membrane structure, especially in the brain. In the context of food and dietary sources, here’s some more info you should know.
Phosphatidylserine is found in varying amounts in many foods. In the past, the primary supplemental source was bovine cortex—aka cow brain. Due to health concerns about diseases like mad cow disease, most commercial phosphatidylserine now comes from soy lecithin or sunflower lecithin instead of actual cow brain.
Organ Meats (think liver and kidneys): Organ meats contain the highest concentration of phosphatidylserine and also provide protein, vitamin A, several B vitamins, iron, folate, copper, and selenium. This one is the most bang for your buck.
Soybeans: The primary plant-based source of phosphatidylserine and a provider of all the essential amino acids—the building blocks of protein.
Meat: Particularly in chicken and beef
Fish: Especially mackerel and herring, which can also help you load up on omega-3 fatty acids.
Eggs: Present in the yolk alongside iron, potassium, and magnesium.
Phosphatidylserine that we gain from eating through foods is potently absorbed in the human body. But even at a high absorption rate, it’s challenging to get the daily optimal doses between 100mg and 300mg.
Some individuals have reported gastrointestinal issues, including stomach upset, nausea, and diarrhea. The symptoms are generally mild and can be treated by taking the supplement with food or adjusting the dosage.
Another less common side effect of phosphatidylserine is insomnia or disrupted sleep patterns. Phosphatidylserine plays a role in the secretion of certain neurotransmitters and hormones, which might affect a person’s sleep pattern.
If you find yourself tossing and turning instead of getting a visit from the sandman himself, try adjusting the time when you take the supplement. Taking it earlier in the day could potentially alleviate sleep disturbances.
Phosphatidylserine may interact with certain medications, including anticholinergic drugs, affecting their efficacy. It can interfere with the absorption of anticholinergic drugs, potentially reducing their therapeutic effects.
Combining phosphatidylserine alongside blood thinners or other medications should be taken with caution as it may lead to unforeseen interactions. Contact your healthcare provider if you want to add phosphatidylserine to your routine.
While phosphatidylserine is generally considered safe when taken in recommended dosages, minor side effects, including insomnia, stomach upset, headache, and dizziness, have been reported.
Yes, phosphatidylserine has been studied for its potential to enhance cognitive function and reduce symptoms of brain fog.
Brain fog often manifests as confusion, lack of mental clarity, and forgetfulness.
By taking phosphatidylserine supplements, it may promote brain health, improve focus, and help alleviate these symptoms.
Some users have reported that taking phosphatidylserine, especially in higher doses closer to bedtime, can affect sleep patterns and even cause insomnia.
On the other hand, phosphatidylserine might help regulate the body’s internal clock and improve sleep in certain situations
If you’re aiming for consistent benefits from phosphatidylserine, then daily dosing is recommended to gauge the supplement’s effectiveness.
For optimal results, speak with your doctor first.
Phosphatidylserine could be like a software upgrade for the aging brain! It’s a vital nutrient that declines with age but can be replenished through diet and supplements. Restoring phosphatidylserine levels may help improve memory, focus, learning, and other cognitive abilities as we age.
So, whether you go hard on the mackerel or find a supplement that tickles your fancy, keeping your phosphatidylserine levels up could potentially give your mind the extra processing power it needs.
As always, please speak with your doctor to find the best plan for you.