Talk to a Registered Dietitian and use INSIDER20 for 20% off!
Talk to a real Dietitian for only $99: Schedule Now
This post contains links through which we may earn a small commission should you make a purchase from a brand. This in no way affects our ability to objectively critique the products and brands we review.
Evidence Based Research To fulfill our commitment to bringing our audience accurate and insightful content, our expert writers and medical reviewers rely on carefully curated research.
Read Our Editorial Policy
Creatine is likely one of the most researched and effective sports supplements on the market today.
Primarily, it is used to enhance muscle growth and improve athletic performance, especially during intense exercise. This is thanks to creatine’s ability to speed up muscle recovery, growth, and energy use by the muscle cells.
Since creatine is so well-researched and commonly used by athletes—casual and competitive alike—we have a pretty definitive idea of how much you should take.
The short answer is that if you want to supplement with creatine, you should be taking about 5 grams per day.
However, there is a specific protocol for the “loading phase” that you need to follow when starting.
How do you do it, and why is this necessary? We’ve got all the answers below, as well as a rundown of the benefits of creatine.
Creatine is an amazing compound that provides a variety of benefits for athletes. However, we don’t consume or synthesize it in spades.
The body’s liver, pancreas, and kidneys can make about 1 gram of creatine per day, and the typical omnivorous diet also provides about 1 gram of creatine.
This works out perfectly since the average person should consume around 2 grams of creatine per day, making this level of creatine intake sufficient for most individuals.
However, if you are an athlete, it is recommended to consume up to 5 grams of creatine per day to experience all its benefits.

But what does creatine do? Well, we’ll dive deeper into that later on, but we’ll give you the spark notes here.
If you’re looking to start taking creatine supplements, though, you need to follow a particular protocol to get the most out of this supplement as quickly as possible.

Getting your creatine dosage correct is important if you want to get the most benefits out of this supplement.
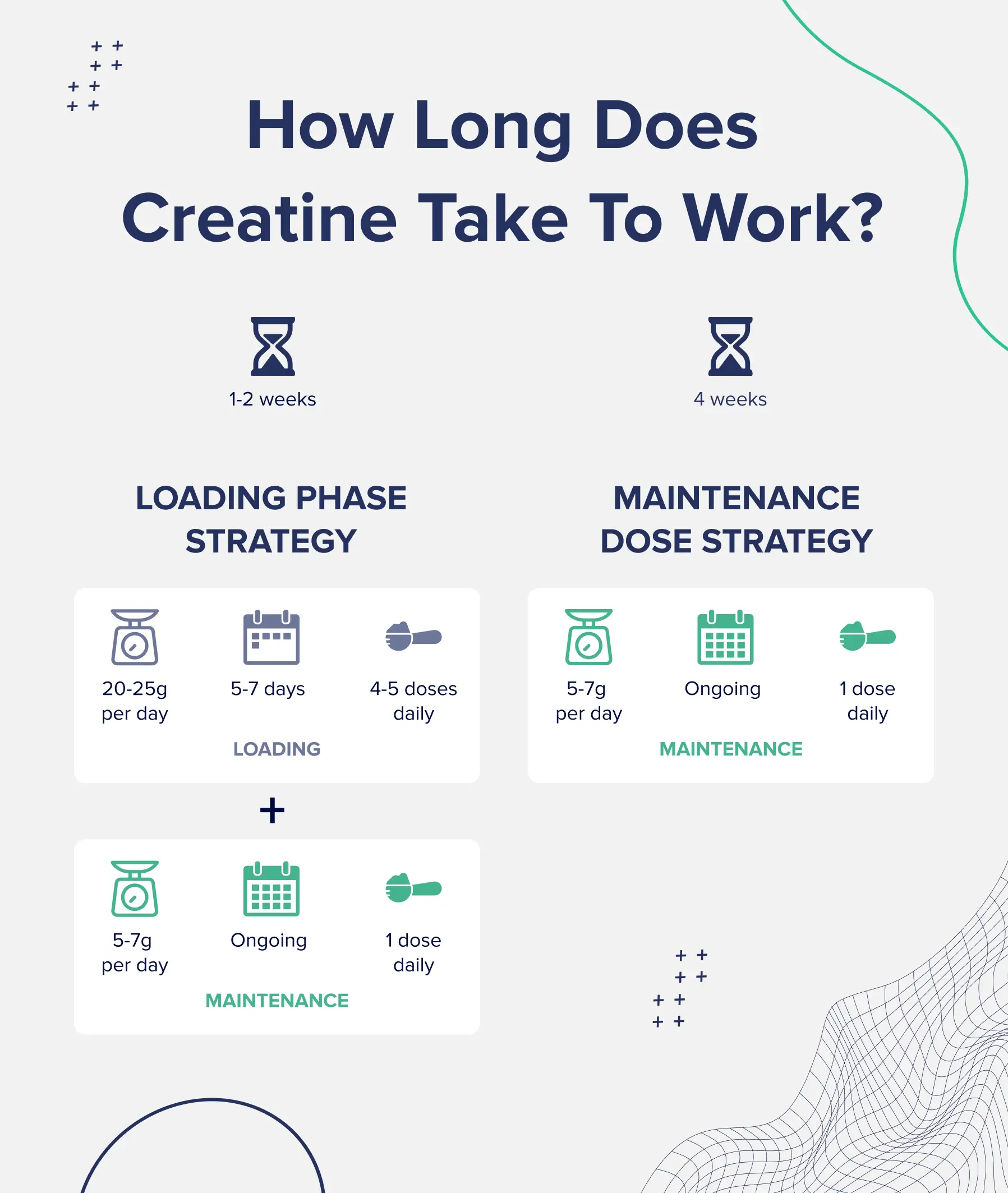
Per the existing scientific literature on the subject of creatine supplementation, there are two recommended strategies.
Neither strategy is technically “better” than the other, but which one you choose depends on your goals.
With the loading phase strategy, you will start your creatine supplementation by taking a higher dose.
The standing theory with this strategy, per the scientific literature, is that loading with a higher initial dose will more rapidly increase creatine stores in your muscles, allowing you to reap the benefits of this supplement more quickly.
This is an optimal strategy for athletes who need to see a more rapid increase in performance or muscle growth within a shorter period of time––around 20 to 30 days.
If you want to try this strategy, the creatine loading phase takes place in the first week of supplementation.
To start, you will take 20-25g of creatine (or 0.3g of creatine per kilogram of body weight) daily for 5-7 days. You can split these into 5g servings––taken with a glass of water or in your protein shake––throughout the day.
Once you have completed this initial loading phase, you can transition to a maintenance dose of around 3-5g of creatine per day (or 0.1g of creatine per kilogram of body weight).
With a higher daily dosage of 20-25g per day, you may notice some digestive issues such as bloating or upset stomach.
If this occurs, you might want to scale back the loading dose or consider trying the maintenance dose strategy instead.
The non-loading maintenance dose strategy appears to be just as effective as the loading phase strategy and is perfectly suited for athletes at any level.
This is also ideal for individuals who intend to take creatine for a long period of time.
The only caveat is that it will take longer to see results in comparison to the loading strategy.
With a maintenance dose, you can take 5g of creatine per day or 0.1g per kg of body weight.
A small amount of research has been carried out with the specific intent of investigating the impact of creatine supplementation on females throughout the lifespan.
This research indicates females in all stages (post-pubertal, menses, pregnancy, post-partum, perimenopause, and postmenopause) respond well to creatine dosing strategies that use a loading phase.
In women, creatine supplementation can help increase athletic performance, improve brain health, increase fat-free mass, increase bone density, and even improve pregnancy outcomes.
There is also one study that indicates creatine monohydrate loading phases may offset exercise performance decreases that can occur during high hormone phases, such as the luteal phase.
So, regardless of your biological gender, the current research indicates that biological men and women can both tolerate––and that women may even benefit from––loading phase doses as well as traditional maintenance dosing throughout the lifespan.
Now that you know how much to take, let’s talk about some of the potential health concerns people have with creatine.
As we’ve stated several times, creatine is an extremely heavily studied compound. There are very few studies that demonstrate there are health problems associated with prolonged (six months or longer) creatine supplementation.
With that said, individuals who suffer from kidney dysfunctions, liver disease, or high blood pressure are advised not to take creatine.
If you have any concerns about taking creatine due to an existing illness, consult your primary care physician.
Now that you know how to take creatine, let’s dive into some of the reasons why you should take creatine.
We know that creatine supplementation is one of the most effective and safest ways to improve athletic performance.
But did you know creatine may also improve brain health and prevent age-related declines in both brain function and muscle mass?
Here are all the benefits of creatine that science has been able to discover so far.
Creatine is a proven and safe supplement for enhancing lean body mass, particularly in healthy young individuals.
Here’s how it works:
It also shows promise for injury prevention, but further research is needed, especially in older populations and those with muscular diseases.
Creatine replenishes ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of our cells, leading to sustained energy levels during exercise, particularly high-intensity exercise. This results in improved strength and power output, as demonstrated by studies on elite athletes, including elite Brazilian soccer players.
Studies suggest that creatine supplementation may reduce the risk of sports-related injuries, including cramping, dehydration, muscle tightness, strains, and various contact and non-contact injuries, particularly in college football players.
Creatine accelerates exercise recovery by promoting cell repair and growth, preserving lean tissue mass, and preventing the breakdown of muscle protein. It proves beneficial during immobilization due to injury or age-related decline.
Creatine exhibits potential in preventing sarcopenia and dynapenia, preserving and increasing muscle mass and strength in aging individuals. It also enhances bone mineral density and reduces the risk of falls, addressing various aspects of age-related decline.
In addition to physical benefits, creatine positively influences brain function and cognitive processing. It aids recovery from trauma, such as traumatic brain injury, by meeting the energy demands of brain cells. Long-term supplementation is essential for noticeable impacts on brain health.
The optimal creatine dosage sits around 5 grams per day unless you’re doing a loading phase. Then, you will take around 20-25g of creatine per day (in four separate doses throughout the day) for 5-7 days. Consuming 10g of creatine per day for an extended period is not likely to provide you with extra benefits.
Creatine is generally safe, but if you have kidney concerns, it’s wise to tread carefully. Individuals with kidney issues or impaired kidney function should approach creatine with caution, as excess creatine could potentially strain the kidneys. Always consult with your healthcare provider if you have pre-existing kidney conditions.
If you experience an increase in weight, do not be alarmed or stop taking creatine. Weight gain can occur when taking creatine since water is being pulled into your muscle cells, and you are growing muscle more rapidly. This is a good thing! Enjoy the new muscles. However, do not take creatine if you have existing kidney or liver concerns or have high blood pressure.
Taking creatine correctly is key to maximizing its benefits. The recommended daily dose is around 5 grams. When starting, there’s a loading phase where you take 20-25g daily for 5-7 days, then transition to a maintenance dose. Alternatively, you can skip the loading phase and stick to a consistent 5g per day, which is ideal for long-term use. Adjust based on your goals and your body’s response.