This post contains links through which we may earn a small commission should you make a purchase from a brand. This in no way affects our ability to objectively critique the products and brands we review.
Sustainable Eating: 12 Sustainability Certifications to Look For
Evidence Based Research To fulfill our commitment to bringing our audience accurate and insightful content, our expert writers and medical reviewers rely on carefully curated research.
Read Our Editorial Policy
If you’re passionate about protecting the environment, you’ve likely made the switch to greener cleaning products, are up on your recycling rules, and may be no stranger to a compost pile.
But what about when it comes to the food you buy? As we generally eat three meals per day, seven days per week, shopping with sustainable eating in mind is one of the best ways to vote with your dollar.
By spending your money on sustainably produced, organic, locally sourced, or ethically farmed food, you are essentially “voting” for practices and companies that support those ideals.
Sustainability in the food system isn’t just about using recyclable packaging—a sustainable food brand will also prioritize animal welfare, organic or regenerative farming, ethical practices, and worker welfare.
These 12 sustainability certifications are great options to keep an eye out for, as they encompass all of those factors.
What Do Sustainable Certifications Mean?
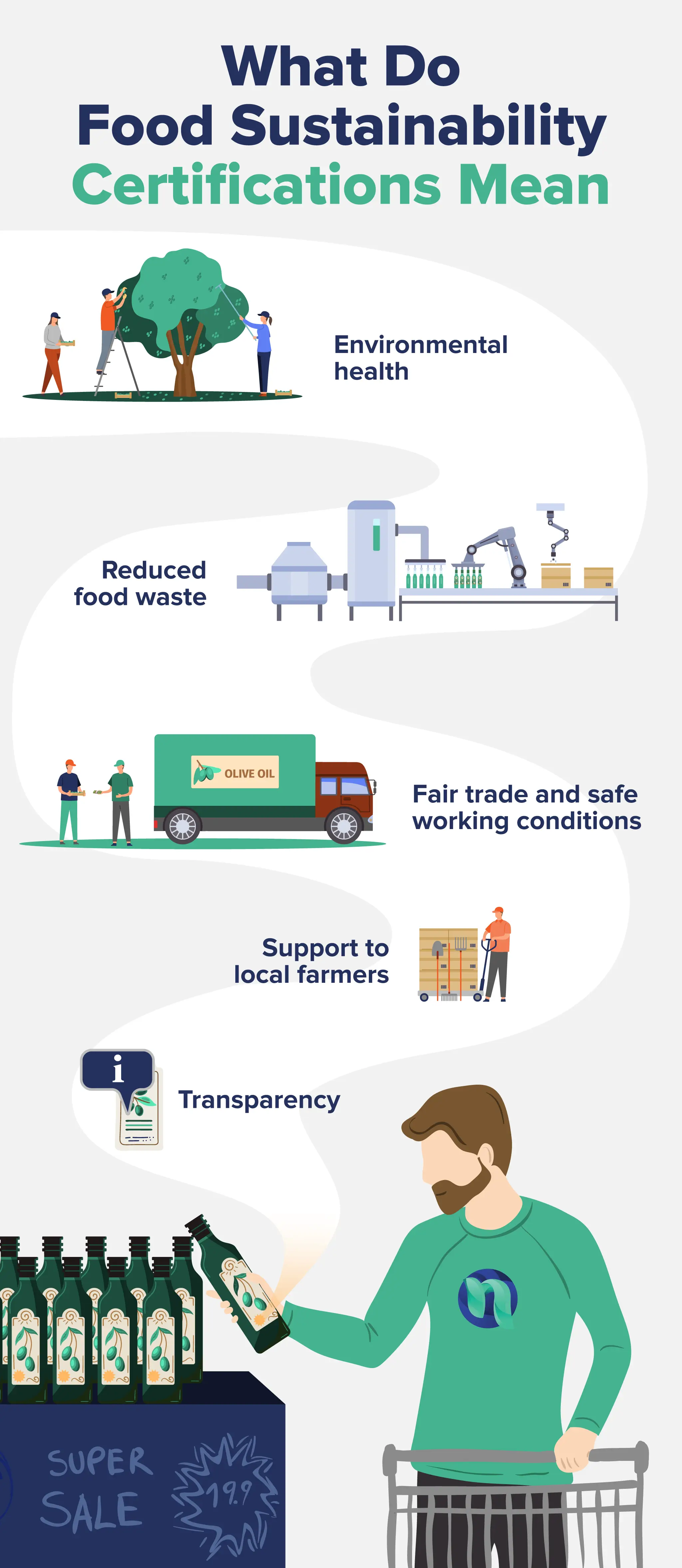
Sustainable food refers to food that has been produced in ways that prioritize long-term environmental, social, ethical, and economic standards.
Sustainability certifications are given by third-party organizations that assess farmers and food producers based on criteria such as:
- Environmental Responsibility: Sustainable farming practices that reduce environmental harm, including regenerative farming, organic farming, water conservation, biodiversity promotion, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and soil health conservation.
- Animal Welfare: Prioritizes the humane treatment of animals, such as pasture-raised, grass-fed, and free-range farming with healthy diets and getting treated justly.
- Fair Labor: Ensuring workers are treated fairly, paid reasonable wages, and provided safe working conditions.
- Economic Sustainability: Supporting local farmers, communities, and economies by promoting fair trade and ensuring the sustainability of small-scale farmers and producers.
- Transparency: Providing clear information about the origins and methods of food production, allowing consumers to make informed choices.
Sustainable food brands will aim to balance environmental health, smaller-scale economic health, ethical production, and social responsibility. Purchasing sustainable food brands can be one way that you play a part in addressing major global concerns like climate change, food insecurity, and resource scarcity.
Sustainability Certifications to Look for When Food Shopping

You won’t see all of these certifications on each food product, as some are very specific. For example, the Marine Stewardship Council applies to sustainable seafood, while Certified Grassfed will only be on beef products.
1. Certified B Corp
If you want a one-stop-shop certification for ethical and sustainable food practices, see if they are a Certified B Corp.
Certified B Corporations are businesses that focus on environmental and social responsibility. To get certified, a company will be scrutinized on factors like community values, conscious environmental choices, carbon footprint, supply chain transparency, and accountability.
When it comes to food sustainability, B Corps brands work to minimize their environmental footprint through sustainable sourcing, organic farming, and reducing packaging waste and greenhouse gas emissions. They also focus on organic and fair trade ingredients, promote fair labor practices, and support community development. Some notable Certified B Corps in the food industry include Numi Organic Tea, Ben & Jerry’s, Danone, Alter Eco, Patagonia Provisions, Cabot Creamery, Tony’s Chocolonely, King Arthur Baking, Once Upon a Farm, Gotham Greens, and Lundberg Family Farms.
2. Regenerative Organic Certified
Regenerative Organic Certified (ROC) is a newer sustainability certification that goes beyond “organic.” A farm that is regeneratively organic certified means that it meets the highest standards for soil health, animal welfare, and social fairness.
It has the same principles as organic farming (like prohibiting synthetic pesticides, herbicides, fertilizers, GMOs, and hormones) but goes further by promoting regenerative farming practices.
Regenerative farming aims not only to avoid environmental harm but also to actively restore and improve ecosystems while supporting farm workers and animal welfare.
With practices like no-till or low-till farming, crop rotation, cover cropping, and composting, one of regenerative farming’s primary aims is to restore soil health.
ROC also has stringent guidelines for the humane treatment of farm animals, emphasizing practices that ensure animals have access to natural behaviors, like grazing on pasture.
Some food (and supplement) brands that have achieved Regenerative Organic Certification are Dr. Bronner’s, Ancient Nutrition, Patagonia Provisions, Nature’s Path, Guayaki Yerba Mate, Harmless Harvest, La Tourangelle, Mountain Rose Herbs, Navitas Organics, Purely Elizabeth, Erewhon Market, Canyon Coffee, and Thrive Market.
3. Climate Neutral Certified
Climate Neutral Certified verifies a brand’s efforts to achieve net-zero carbon emissions for their products and operations. Businesses must measure, reduce, and offset their carbon footprints, contributing to global efforts to combat climate change.
After measuring their carbon footprint, companies are required to implement strategies to reduce and then offset their emissions. This may involve improving energy efficiency, transitioning to renewable energy sources, optimizing logistics, and sourcing materials more sustainably.
To maintain Climate Neutral Certification, companies must undergo an annual recertification process. This involves reassessing their carbon emissions, documenting their reduction efforts, and ensuring that they continue to offset their emissions adequately.
Food brands that are Climate Neutral Certified include ALOHA, Alter Eco, Burgeon Beer, Jiant Kombucha, Juneshine, Numi Organic Tea, and Thrive Market.
4. SCS Sustainably Grown® Certification
The Sustainably Grown Certification by SCS focuses on sustainable agricultural practices and aims to improve the environmental, social, and economic performance of farms.
This certification is comprehensive when it comes to sustainable food choices, as it evaluates farms based on practices that promote soil health, water conservation, biodiversity, pollinator protection, climate adaptation, and labor rights.
It also assesses fair trade practices, wages, workplace safety, community engagement, climate neutrality, air quality, crop and pest management, energy efficiency, transparency, and more.
This certification applies to a wide variety of agricultural products, including fruits, vegetables, grains, and other crops.
5. Fair Trade Certifications
There are many different fair trade certifications that have similar names, so we’ll include them together here.
Fair trade means both farmers and workers receive a fair price for their labor and products. A fair trade certification will also ensure that safe working conditions are met and that sustainability practices are prioritized, such as deforestation-free farming methods or reducing carbon footprints.
Fairtrade brands may also be involved in local communities, providing education, healthcare, and infrastructure.
The main fair trade certifications you may see include:
- Fairtrade International: The most widely recognized Fair Trade certification, setting global standards for fair wages, labor conditions, environmental sustainability, and economic empowerment of small-scale farmers and workers. Food products you may see with this certification include coffee, cocoa, tea, bananas, and sugar.
- Fair Trade USA: The leading Fair Trade certifier in North America, Fair Trade USA focuses on fair wages, worker empowerment, and sustainability, with food products including coffee, chocolate, dairy, seafood, vegetables, fruit, and more.
- Fair for Life: A certification program created by the Swiss Bio-Foundation, administered by Ecocert, that covers Fair Trade and social responsibility across many industries, including food, textiles, agriculture, and cosmetics.
- World Fair Trade Organization (WFTO): A global network of Fair Trade businesses, certifying entire organizations, not just products. WFTO certifies a wide range of brands, from food to fashion to manufacturing.
- Equal Exchange: A fair trade organization known for its transparent and ethical sourcing of products like coffee, chocolate, tea, bananas, nuts, and dried fruits. It focuses on small-scale farmers and is structured as a worker-owned cooperative, meaning the employees own and control the business.
6. Rainforest Alliance Certified
Rainforest Alliance Certified is also in the lane of fair trade but is a bit more specific.
You’ve probably seen that cute little green frog logo on bags of coffee or chocolate bars, which means that the product has met standards to protect forests, improve the livelihoods of farmers and forest communities, and promote human rights.
Certified farms must conserve wildlife habitats, protect native species, and avoid deforestation. This includes practices like maintaining buffer zones around water bodies and preserving forested areas.
For example, one such buffer zone is Indonesia’s Bukit Barisan Selatan National Park, where Rainforest Alliance farmers planted 45,000 trees in the area bordering the park, including plants consumed by the critically endangered Sumatran elephant.
Certified products, such as coffee, cocoa, palm oil, bananas, and tea, are traceable through the supply chain, ensuring that the ethical and sustainability criteria are maintained and accessible by consumers.
7. Marine Stewardship Council/Seafood Watch
The Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) is an international nonprofit that certifies sustainable seafood and focuses on reducing overfishing and preserving healthy oceans, lakes, and rivers.
MSC-Certified Fisheries must demonstrate that they manage fish stocks sustainably, minimize environmental impact and harm, and are well-managed. Seafood products from MSC-Certified fisheries carry the MSC blue ecolabel, which signifies that the seafood comes from an environmentally responsible and sustainable fishery.
Seafood Watch by the Monterey Bay Aquarium is similar, although it’s not an official certification program. It uses a color-coded system to provide recommendations for consumers, chefs, and businesses on which seafood products are sustainable, overfished, or caught using harmful practices.
8. USDA Organic
As the first widely recognized U.S. standard for making farming more environmentally friendly, “USDA Organic” prohibits synthetic pesticides, herbicides, fertilizers, GMOs, and hormones.
A USDA Organic seal does not always mean a product or brand is entirely sustainable, but it’s certainly a good start.
Not using synthetic pesticides and fertilizers encourages healthier soil, which is a tenet of sustainable farming. USDA Organic also requires that livestock raised for organic products must have access to the outdoors, be fed organic feed, and not be treated with antibiotics or growth hormones.
However, one of the main criticisms of USDA Organic is that it tends to favor larger operations, as the costs associated with maintaining certification can be impossible for smaller farms to meet.
9. Demeter Biodynamic
Demeter Biodynamic certifies that farms function as biodynamic, living organisms. Biodynamic farming goes far beyond organic, emphasizing the interrelationship of soil, plants, animals, and humans, often using spiritual and holistic principles like lunar cycles and planetary placements to guide farming practices. (The name Demeter is telling of this, as Demeter is the goddess of agriculture, fertility, harvest, and the earth.)
The Demeter Biodynamic certification ensures that a farm is self-sustaining and promotes biodiversity, soil health, and sustainable farming practices while avoiding synthetic chemicals, pesticides, and GMOs.
Biodynamic farms focus on the ethical treatment of animals, support local economies, produce their own compost and animal feed, and rely on their resources to maintain soil fertility and pest management.
10. Soil & Climate Initiative
The Soil & Climate Initiative is a newer regenerative-focused certification focusing on soil health, biodiversity, water quality, climate resiliency, and small farm economics.
Getting Soil & Climate Health Initiative Verified means that a farm has earned third-party verification that they support these practices.
Some of the key factors involved in this certification are minimizing soil disturbance, reducing synthetic inputs, nurturing live roots, year-round soil coverage, appropriate livestock integration, and maximizing diversity.
11. Animal Welfare Certified
The Global Animal Partnership (GAP) created the Animal Welfare Certified standards, which differ slightly by animal species. However, all animal welfare standards require the animals to have outdoor access, healthy diets, enriched environments, and support for emotional well-being.
Farms and brands are scored on a scale of 1 to 5+, with scores of 4 or above meaning the animals are pasture-raised year-round, while scores of 5+ mean the animals spend their entire lives on the farm.
For example, a cattle farmer could get a 5+ rating if the cows are 100% pasture-raised, spend their entire life on the farm (no transportation), are naturally weaned, and have a 75% minimum vegetative cover on their pasture.
While this is more a certification for animal welfare and ethics, it also translates to sustainability. This is especially true for pasture-raised animal farming, which improves soil health with nutrient cycling (aka returning nutrients to the soil through manure), boosts biodiversity, and uses rotational grazing systems that allow for healthy grass growth.
12. Certified Grassfed
A similar certification is Certified Grassfed by A Greener World, which applies specifically to beef. It ensures that cattle are raised on 100% grass-fed and foraged diets on an open pasture or range.
Although other grass-fed labels exist, this certification also ensures that farms are managed according to the highest welfare and environmental standards on an independent farm.
It also requires country of origin labeling, supply chain traceability, responsible antibiotic use, prohibits deforestation, and annual audits by third-party organizations.
Sustainable Eating FAQs
What is certified sustainable food?
There is no single certification for sustainable eating, but there are many organizations that provide third-party certifications that verify different aspects of sustainability. They typically include some or all of the following factors: environmental health (such as water conservation, land management, regenerative farming, soil health, and more), social responsibility, ethical practices like fair trade and safe working conditions, and support for the local community. Sustainable food production also uses practices to reduce food waste, including reusing or composting food scraps.
What is the best certification for sustainability?
There is no single best certification for food sustainability, but some of the best include Certified B Corp, Regenerative Organic Certification, SCS Sustainably Grown® Certification, Soil & Climate Initiative, and Fairtrade International.
What food is most sustainable?
The most sustainable eating choice is to grow your own food, which is about as “eating local” as you can get. The next best is food purchased at your local farmer’s market. In general, plant-based foods are more sustainable than meat and dairy (with the exception of nuts like almonds and pistachios, which require a lot of water). Beans, lentils, and peas are particularly sustainable sources of plant-based protein, as they don’t require as many resources as animal protein. Regarding meat and dairy, anything that has the Regenerative Organic Certification will be a more sustainable option.
How can you eat sustainably?
Sustainable eating habits include growing your own food, buying at the local farmers market, reducing food waste at home, minimizing processed foods, purchasing products in sustainable food packaging, shopping at your local grocery store (rather than purchasing online), or joining a CSA (Community Supported Agriculture) program that supports a local farm. You can also reduce food waste by meal planning and eating plant-based meals when you can unless you are purchasing sustainably raised animal products.








