Try our favorite, clean protein powder: See our top pick →
Try our favorite, clean protein powder: See our top pick →
This post contains links through which we may earn a small commission should you make a purchase from a brand. This in no way affects our ability to objectively critique the products and brands we review.
Evidence Based Research To fulfill our commitment to bringing our audience accurate and insightful content, our expert writers and medical reviewers rely on carefully curated research.
Read Our Editorial Policy
Our hair and nails are a few of the key indicators of our health.
Among the most common complaints people have when it comes to these more aesthetic parts of our bodies are brittle nails and thinning hair.
While certain thyroid disorders and diseases can negatively impact the health of our hair and nails, sometimes it’s just plain old aging, poor diet, or even stress.
To combat this, health and wellness gurus have touted the benefits of biotin not only for nail growth but also for hair health.
According to these online experts and some anecdotal reports, this supplement can supposedly turn your limp locks into a magical mane.
But does it really work? Well, we looked into it and found that while biotin isn’t a magical cure-all for hair growth, it could have some positive benefits. Here’s what we found.
We’ll state it right off the bat: there is no scientific evidence that proves there are any sort of benefits of biotin supplementation for hair growth in healthy individuals.
However, there is evidence that taking biotin can be beneficial for those experiencing a biotin deficiency.
It is very rare to have a biotin deficiency. However, if you are experiencing hair loss or thinning hair (alopecia), skin problems such as eczema and seborrheic dermatitis, conjunctivitis, or multiple neurological disorders such as depression, lethargy, or seizures, it may be worth a visit to your doctor to figure out if you have a biotin deficiency.
In a systematic review of 18 cases that studied the effects of biotin supplementation, it was found that participants did see improvements in their hair and nails. The caveat?
The majority of participants either were known to have a biotin deficiency or had a history of poor hair and nail growth that indicated other underlying issues.
So, in effect, if you have self-perceived thinning hair, poor nail growth, uncombable hair syndrome (yes, that is a clinical diagnosis!), or other hair and nail problems, you may see some benefits from taking biotin.
Biotin, also known as vitamin B7, is a water-soluble vitamin found in the B vitamin complex family.
As opposed to fat-soluble vitamins, water-soluble vitamins do not build up in the body and so need to be regularly consumed to keep levels normal.
Like all B vitamins, biotin helps to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, and amino acids, which are the building blocks of protein.
Specifically, biotin plays a role in keratin production; keratin is what makes up our hair and nails.
The theory goes that by supplementing with biotin and even putting it in topical beauty products, the vitamin may promote hair growth by stimulating keratin production, thereby increasing the growth rate of nails and hair follicles.
As previously mentioned, the evidence thus far indicates that biotin is primarily effective for individuals experiencing poor nail growth, hair thinning, and hair loss.
If your hair and nails are relatively healthy, you probably won’t see many benefits (if any).
If you are experiencing noticeable hair loss, make an appointment to see a doctor to determine if there are any underlying problems. It could be a biotin deficiency, but it could also be something more serious.
If you simply want to try to boost your hair growth, there is some anecdotal evidence from women complaining of hair loss who have reported improved hair growth when supplementing with biotin. If that’s you, here’s how much you should take.
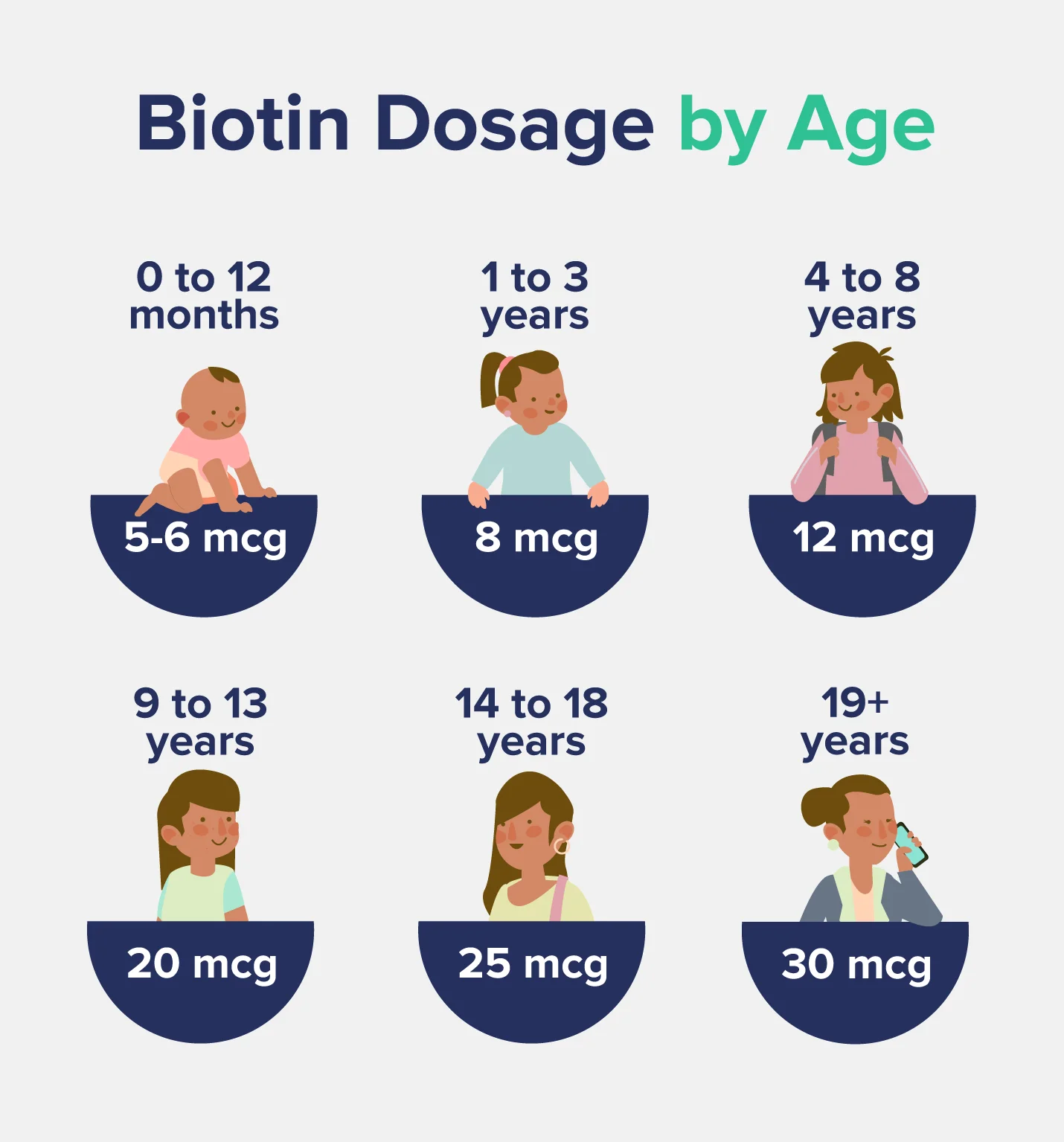
The Food and Nutrition Board sets either an RDA (Recommended Dietary Allowance) or an AI (Adequate Intake) for vitamins and minerals.
The RDA is the average daily nutrient intake level needed to meet the requirements of 97-98% of healthy adults.
The AI is an intake level that is assumed to be nutritionally adequate for most people, but the available evidence is insufficient to develop an RDA.
The Food and Nutrition Board has not found sufficient data to set an RDA for biotin, which is why you’ll only see AIs for this nutrient.
| Population | Biotin AI |
| Birth to 6 Months | 5mcg |
| Infants 7–12 Months | 6mcg |
| Children 1–3 Years | 8mcg |
| Children 4–8 Years | 12mcg |
| Children 9-13 Years | 20mcg |
| Children 14-18 Years | 25mcg |
| Adult Males 19+ | 30mcg |
| Adult Females 19+ | 30mcg |
| Pregnancy | 30mcg |
| Lactation | 35mcg |
The AI for adults is 30 micrograms (mcg) per day. However, many supplements contain much more.
This is usually not a problem, but there can be some unintended side effects from taking too much biotin.
There is no UL (Tolerable Upper Intake Level) for biotin. However, some people experience mild side effects like nausea and digestive issues––especially at high doses––as well as breakouts in acne-prone people.
Consuming more than the recommended daily amount—just 30mcg for adults—can cause false results in some laboratory tests, including hormone, thyroid, pregnancy, and vitamin D tests.
So, make sure to let your doctor know if you’re taking a biotin supplement to support hair and nail growth or address suspected nutritional deficiencies.
If you are eating a balanced diet of fruits and vegetables, varied protein sources, and complex carbohydrates, you likely are getting enough biotin.
However, if you want to naturally increase your intake of biotin, there are some foods higher in this essential vitamin:

Some individuals report anecdotal evidence that biotin can help your hair grow more quickly and keep it healthier. However, there is no scientific evidence that biotin can increase hair growth in healthy individuals.
For individuals that have noticeable hair loss, increasingly thinning hair, or have been diagnosed with a condition that causes hair loss or hair thinning, you may benefit from supplementing with biotin.
The Food and Nutrition Board has not set an RDA (Recommended Dietary Allowance) for biotin. However, there is an AI (Adequate Intake) level for biotin. For adults, this is around 30 micrograms (30mcg). You can typically get this amount of biotin from a healthy and balanced diet. If you want to increase your biotin intake, most supplements contain a much higher level of biotin than 30mcg.
While there is no UL (Tolerable Upper Intake Level) for biotin, consuming more than the recommended daily amount can lead to some negative side effects. This can be as mild as some nausea and digestive issues, but at higher doses can lead to breakouts in acne-prone people. Let your doctor know if you’re supplementing with biotin before taking any laboratory tests since higher levels can cause false results.
Since there is not enough research yet to determine an RDA for biotin and there is no UL, there are no contraindications for taking biotin every day. Just be mindful of the dosage and do not exceed the recommended servings per day.
Subscribe now and never miss anything about the topics important to you and your health.